Service management for business teams
About this guide
For this guide to be effective, we recommend reading the ITSM Solution Delivery Guide and Overview of ITSM use cases and reference architecture.
The guide provides a comprehensive overview of delivering and implementing Atlassian tools and IT Service Management (ITSM) using a standardized delivery process through an opinionated view, leveraging best practices. It is written for those about to set up a Jira Service Management (JSM) implementation project.
This guide aims to make customers happy through simpler ITSM implementations. The guide will be regularly updated with new information and feedback to ensure that it stays current and effective.

Use case: Service Management for Business Teams
Introduction
JSM is a powerful tool that can be used by business teams to improve their service delivery and streamline their workflows, automate tasks, and track their progress in real-time. This helps to increase efficiency and productivity, reducing the risk of errors and delays.
One of the main benefits of using JSM is that it is a low-code platform, which means that business teams do not need programming skills to set it up. The platform is user-friendly and easy to configure, making it accessible to all team members, regardless of their technical expertise.
With JSM, you get real-time insights into your service delivery, enabling you to make data-driven decisions and continuously improve your processes. This can help your teams to deliver better services, increase customer satisfaction, and ultimately, drive business growth.
Problem definition
JSM has proven to be a valuable tool for IT departments, providing a help desk portal and asset tracking features. However, it’s not just IT departments that can benefit from this platform. Business teams that provide services to customers also recognize the value of using JSM.
Instead of implementing separate tools or responding to multiple emails, business teams can now collaborate with IT teams on a single platform. Doing so can increase transparency and ultimately deliver more value to their customers.
JSM allows business teams to work together with IT teams, improving communication and reducing silos. With the platform’s powerful capabilities, teams can manage requests, incidents, and problems, all while tracking assets and providing exceptional service.
In short, JSM isn’t just for IT departments. Business teams can also benefit from its features, collaborating with IT teams to provide top-notch service to their customers.
Challenges for Legal teams
Legal teams often serve a supporting function within the company. They are asked to give their opinion on various legal matters in general, but more specifically, they are often asked to review legal agreements. The legal team will need specific kinds of input to ensure that agreement reviews are handled properly. These inputs could be information on who the involved parties are, what are the purposes of the agreement, what deadlines to take into account, and affected markets, etc.
Challenges for HR teams
HR is another example of a team constantly struggling with ad hoc work and multiple input channels. Managing joiners, movers, and leavers is a large undertaking that involves many parts of the organization. There are also various questions and requests that the HR team receives regarding vacations, sick leave, expense reporting, etc.
In an HR onboarding scenario, IT needs to provide the employee with access and licenses in addition to computers and phones. The facilities team needs to ensure that the employee gets a badge so they can enter the office building where they will be working. The line manager must ensure that employment agreements are signed, and a start date is agreed upon. Depending on the type of work, the legal team may even need to vet the employee.
Onboarding is a very clear example of a process with many moving parts, many different teams that need to be involved, and a certain kind of workflow that would benefit from a standardized process.
Challenges for Marketing teams
Marketing departments face various challenges, including campaign management, brand management, content creation and distribution, collaboration, and communication. JSM and Confluence can be used to mitigate these challenges by creating custom workflows, centralized repositories for brand guidelines and campaign information, managing content creation workflows, and facilitating communication and collaboration between team members.
Challenges for Finance teams
Finance teams face many challenges, such as budget management, compliance, and regulatory requirements, data analysis and reporting, collaboration, and communication. JSM, Confluence, and communication tools (for example, Slack) can be used to mitigate these challenges by creating custom workflows and dashboards, centralized repositories for policies and procedures, custom reports and dashboards, and facilitating communication and collaboration between team members.
Common challenges
Juggling all of these tasks using mail, chat, and even spreadsheets, makes it difficult to keep track of everything. Input will come in various forms, and there will often be incomplete information that might prevent work from even starting. Categorization and prioritization become quite manual tasks since there is no centralized overview of work. The overhead of keeping all interested stakeholders up to date can also increase the administrative workload for the teams.
In addition, repetitive tasks without automation support could prevent teams from having enough time to focus on issues that are more strategic and/or create more value.
Another problem is that without a system to keep track of all of this, interactions from the organization with the various business teams can sometimes feel like shouting into the void. Without any SLAs on various kinds of requests or instant feedback on how long a particular type of issue may take to resolve, frustration, misunderstandings, and unnecessary stress is inevitable.
Discovery and solution description
Before beginning with JSM, it is crucial to comprehend how the affected teams currently work and how they log and track their tasks. It is essential to dedicate sufficient time to understand these aspects thoroughly. To achieve this, you can use remote tools or conduct an on-site event with the entire team or key representatives from the team, along with other stakeholders. Including a good mix of representatives from different roles can help cover more use cases in your workshops.
Consider the benefits and ways you can leverage Assets, the native Asset management solution in JSM, to support your use cases and needs. We will dive deeper into the benefits of working with Assets later, when looking into Asset Management for Business Teams.
To set up a solution that benefits the organization as a whole, it is imperative to have a clear understanding of the team, stakeholders, and the needs of the customers who utilize your services. With its low-code platform and easy-to-configure interface, it is accessible to all team members, regardless of their technical expertise, and can help teams to achieve their goals quickly and efficiently. Adding a Service Catalog to the mix can also help streamline the service delivery process and ensure that customers receive the right services. Therefore, investing time in understanding your team’s current work processes and using that knowledge to establish an effective ITSM platform is crucial.
Here are a set of questions that need to be answered. However, go through the “Workshop in a Box” material accompanying this blueprint.
- What are the current workflows for various ITIL practices and processes?
- Are there any tasks that could/should be carried out in a specific way each time?
- Are there repetitive tasks that can be automated? Where are the pain points?
- What touchpoints does the team have with other teams?
- How are they keeping each other and other teams in the loop of what is going on in terms of their commitments?
- What kinds of requests does the team encounter from the organization?
- What are the expectations from the rest of the organization when working with the team (acceptable response times and how long time is needed to solve a certain type of issue?
- What type of automation is being used, and where is it being used?
This kind of discovery work is something that might need to be done in multiple stages or sprints. Focus on a specific area at a time (for instance, an ITIL practice), create an MVP, and then implement and iterate.
Automation
Customers may have some automation or have sporadic areas where they use automation to reduce the repetitive work so their teams can focus on what matters most. JSM provides the ability to use automation globally across projects and products — anyone can build an automation rule in minutes. No code, no bottlenecks - simply select from Atlassian’s wide range of templates.
JSM Templates
A good approach is to start with one of the ready-made Service Management project templates in JSM (such as Finance service management, HR service management, Marketing service management, or Legal service management). The templates will provide a good starting point that you can continue to iterate on to suit your particular needs. In the templates, there are some existing request types that can be used in the organization.
Funnel your work into JSM
For teams that prefer to work with chat tools, like Slack and Teams, there are integrations available in JSM to cover those needs. Using these tools will make it possible for teams to funnel incoming requests from a chat tool directly into an issue in JSM.
Depending on the amount of needed information from the end user, it can be useful to redirect the end user to the portal. We recommend clearly describing the chat channel's purpose and a link to the JSM portal to avoid confusion.
It can also be beneficial to use widgets or issue collectors to get additional feedback from users who don’t normally use the Help center or Service Portal.
The JSM Help Center (and the Service Portals within it) is where your customers go to get information and raise requests. When you sign up for a JSM site, a Help Center for your site gets created automatically. A corresponding Service Portal is automatically created for each service project you create. In each Service Portal, customers might help themselves by searching for information in your knowledge base, or they can raise a request to ask a service project team for help (shift-left approach).
Permissions and security
To be able to confidently work with all kinds of issues in your ESM setup, you want to be sure that information is only available to the people who need it when they need it. The " when " aspect is easy to overlook, but it is important if a person switches managers, for instance. In that case, you want to ensure that any issues regarding that person are automatically connected to the new line manager (approvals, for instance).
JSM and Confluence have a robust set of permission settings, making it easy to tailor solutions that fit your needs. Using permission schemes, the portals can be restricted so that issues are only available to the agents working in the portal. A team for which this might make sense is the HR team. It is possible to get even more granular with issue-level security, where access can be restricted to certain groups/roles in the organization, such as managers.
An example of a use case where you would need even more granular restrictions would be a resignation issue regarding a certain individual. This is an issue that, at least initially, should only be accessible to the line manager of this particular individual. One way to set this up, to minimize the risk that the information is seen by the wrong people, is to configure the company's organizational (people) hierarchy in Assets. You can then create a user picker field with line managers and, using automation, make sure that the relevant manager in Assets is mapped to the manager value in the user picker field. That way, when an individual creates a resignation issue, the issue is automatically restricted to that person’s line manager using the user picker field in the issue security.
For legal and compliance teams, it is possible to restrict issue access to specific individuals or groups. This can be done by using either issue security or user-/group picker fields in conjunction with permission schemes.
Confluence
It is important to “shift left” in JSM and solve issues closer to the issue reporter rather than further down the line. To support this approach, it is recommended to set up a knowledge base (KB) in Confluence that is relevant and updated. By doing so, customers can help themselves and access relevant articles before submitting a request. This frees up your agents’ time to focus on more complex issues, ultimately resulting in improved efficiency and productivity.
Confluence comes in two flavors with regard to JSM:
- As part of the JSM solution. You get the knowledge base functionality but miss out on some of the Confluence product's features.
- The standard Confluence implementation with a robust feature set in addition to the knowledge base functionality.
To standardize the look and feel of the knowledge base, we suggest using the Knowledge Base templates. This allows teams to quickly and easily document their knowledge articles, further enabling them to shift left and address issues closer to the source.
JSM provides numerous use cases for HR departments. One area where a knowledge base can immediately benefit HR teams is by providing answers to common questions, saving agents time, and improving overall efficiency. Again, shifting left as described above.
Some examples of questions that can be addressed by a knowledge base include:
Employee benefits
Sick pay policies
Vacation time entitlements
Parental leave procedures
Onboarding processes
Payroll procedures
Compliance requirements
Termination policies
Transfer processes
Promotion criteria
There are several other areas that HR teams can consider for their Jira Service Management knowledge base. We recommend you to group them together, and here are some examples of groupings:
- Performance management: Information on how the organization measures, evaluates, and manages performance.
- Training and development: Resources for employees to enhance their skills and career development opportunities within the company.
- Employee relations: Policies and procedures for managing employee complaints, conflicts, and concerns.
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion: Information on the company’s DEI initiatives, policies, and resources.
- Compensation and benefits: Details on salary structures, bonuses, health insurance plans, retirement plans, and other benefits offered by the company.
- Workplace safety: Guidelines on how to maintain a safe work environment and how to report workplace accidents or incidents.
- Company culture and values: Information on the organization’s mission, vision, and values, as well as initiatives and events that promote company culture and engagement.
The finance team also benefits from a robust knowledge base where questions about expenses, representation, taxes, customer accounts, invoicing, etc., can be answered and then shared with the organization as needed.
3rd Party Business Software
In today’s business world, companies rely on a wide range of software applications to manage their operations, improve collaboration, and enhance customer experience. Integrating these applications with JSM can help businesses streamline their processes and provide quality services to their customers. As a consultant, having knowledge about these integrations is crucial in helping businesses optimize their workflows and achieve their goals.
Below are some examples of 3rd party business software to be aware of:
Workday: Workday is a Human Resource Management System (HRMS) that provides a range of features to manage HR-related tasks such as recruitment, payroll, employee performance management, and more. It can benefit HR teams by providing an integrated platform to manage and automate HR processes while also providing insights and analytics to make informed decisions. JSM can leverage Workday’s HR management features to create a seamless employee onboarding experience.
Salesforce: Salesforce is a customer relationship management (CRM) platform that helps sales, marketing, and customer service teams manage customer relationships and track sales leads. It benefits your customer service teams by providing a single source of customer data to help them resolve issues quickly.
Slack: Slack is a team communication and collaboration tool that benefits teams across departments by providing a centralized platform for communication. When Slack and JSM are integrated, you can communicate and collaborate with other teams and customers in real-time, leading to faster issue resolution and enhanced customer support.
HubSpot: HubSpot is a marketing, sales, and customer service platform. JSM can leverage HubSpot’s inbound marketing features to attract and engage customers. HubSpot’s sales and customer service features can help JSM teams manage customer relationships and resolve issues faster.
Solution workflow
The diagram shows the different products and channels that are involved in the solution.
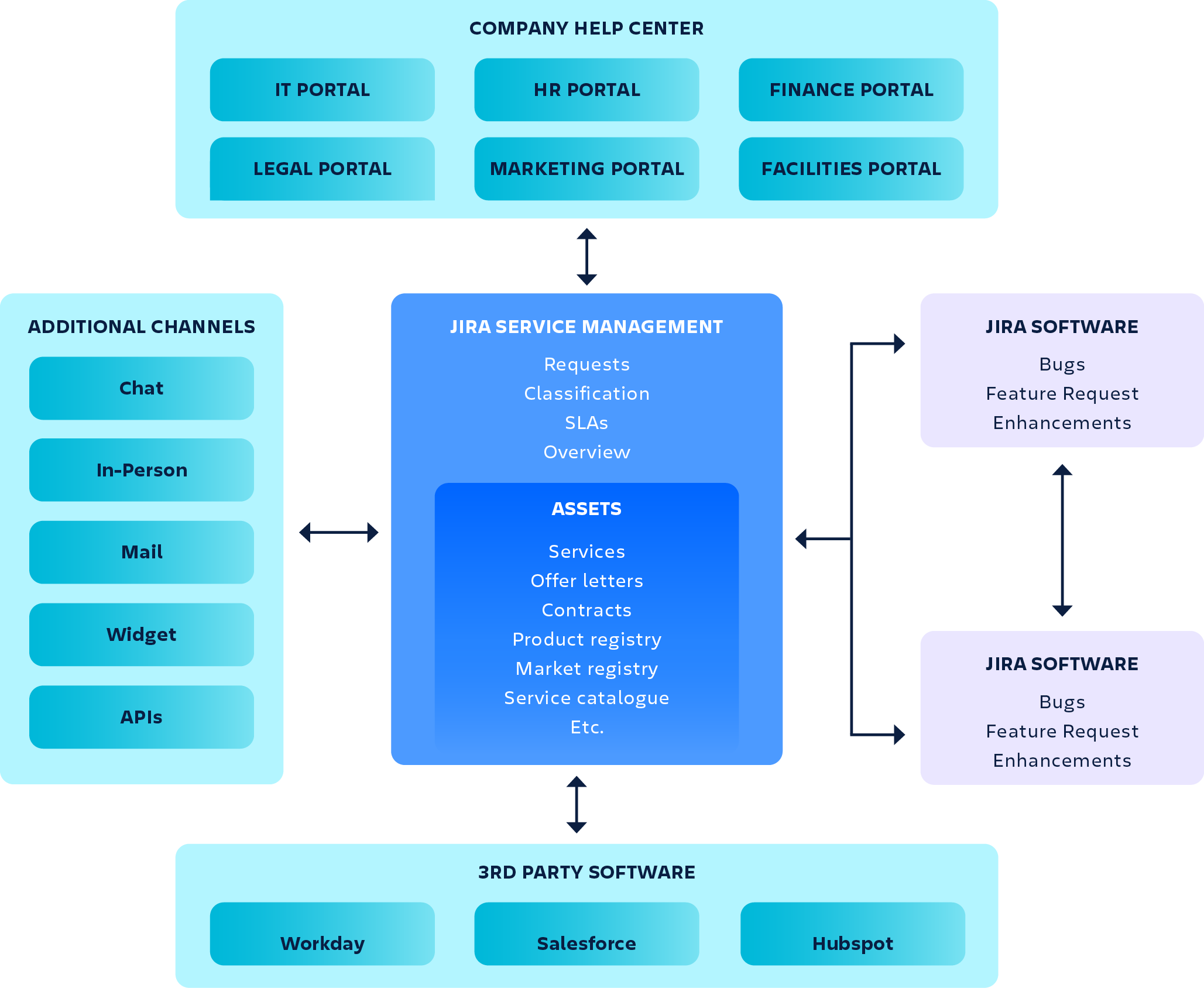
Customers register tickets in one of the channels.*
Agents receive the tickets and respond to the customers (which will trigger a notification in mail or chat).
At any time during the life cycle of the issue, KB articles can be shared with the customers or with the agents handling the tickets.
Once the ticket is resolved, the customer will be notified and the ticket will be closed.
Once the ticket is resolved, the customer will be notified, and the ticket will be closed.
Depending on the outcome of the ticket, additional KBs may be written in Confluence, improvements logged or processes updated.
During the communication process there might be a need to pass information from 3rd party tools to JSM. Jira platform provides a range of APIs that can be used to “build your own” integrations. As a consultant you can also utilize Atlassian marketplace to “bring your own” integrations.
*If the customers do a search in the Help Center or the Service Portal, they may get a hit on a KB article. The article could contain information that resolves the issue, thereby removing the need to register a ticket.
Asset Management for Business Teams
Assets, the integrated Asset Management solution in JSM, already has a proven track record with the IT, HR, and Facilities teams. It helps the teams keep track of various assets and how they connect to people, facilities, etc. But Assets are just as useful to business teams as they are to IT teams.
Legal and compliance teams can use Assets for contracts, offer letters, agreements, information on intellectual property, and as a way to keep track of information on various standards (such as ISO certifications). The information can be connected to issues in JSM. This is particularly useful in an audit situation where the connection between the various standards tracked in Assets and the actions taken to comply with them (issues in JSM), will be investigated.
Marketing teams can use Assets as an inventory of various products offered by the company. Other use cases could involve keeping track of customer segments and markets in which the company is involved. This kind of information is also useful to the legal team. The markets selected in a JSM issue regarding a legal agreement are essential information to decide what laws and regulations to comply with.
The modular structure of Assets makes it easy to get started quickly. Begin with just one or a few teams and some of their use cases. Over time, you can iterate and add more use cases and teams according to your evolving needs.
Affected Services - Asset registry bring value to your business
In addition to the useful features of Assets, JSM also includes a drop-down list called Affected Services. This list can be populated with data from the Asset Management application, which provides detailed information about the different services that your organization offers. By selecting the appropriate service from the drop-down list, users can quickly identify which areas of the organization are affected by a particular issue or incident.
As for other use cases that could apply to the Affected Services field. For example:
- In a support or service desk context, the Affected Services field could be used to identify which service or product a customer is having trouble with. This information could then be used to route the issue to the appropriate team or individual for resolution.
- In a project management context, the Affected Services field could be used to track which services or products are impacted by a particular project. This could be useful for reporting and stakeholder communication purposes.
- In a risk management context, the Affected Services field could be used to identify which services or products are most critical to the organization’s operations. This information could be used to prioritize risk mitigation efforts.
The Affected Services field adds value by providing a quick and easy way to identify which parts of the organization are impacted by a particular issue or incident. This can save time and improve communication, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective resolution of issues.
Admin configuration
Provided that you have done the work outlined in the Discovery and solution description, you should understand how to move on with the following steps in JSM.
- Start by creating a new project using any of the JSM templates for business teams, like the HR service management template.
- Customize your request types and group them into logical categories for the customers
- Add the agents that will be working in the portal.
- Setup Queues for the project.
- Set up Assets to support the findings from your discovery work.
- Create a knowledge base in Confluence. Then use this for KB articles for the customers and documentation on processes and work routines for the agents.
- Modify the workflows so that they correspond to your identified ways of working, and choose what statuses should be made available for the different request types (more information on typical workflows can be found under the Workflow configuration below).
- Set up your Help Center and Service Portal (more information on Help Center and Service Portal 11 configurations can be found under Help Center and Service Portal configuration below).
- Review and adapt any existing automation and add new ones based on your needs. Examples of automation for business and non-tech teams may include:
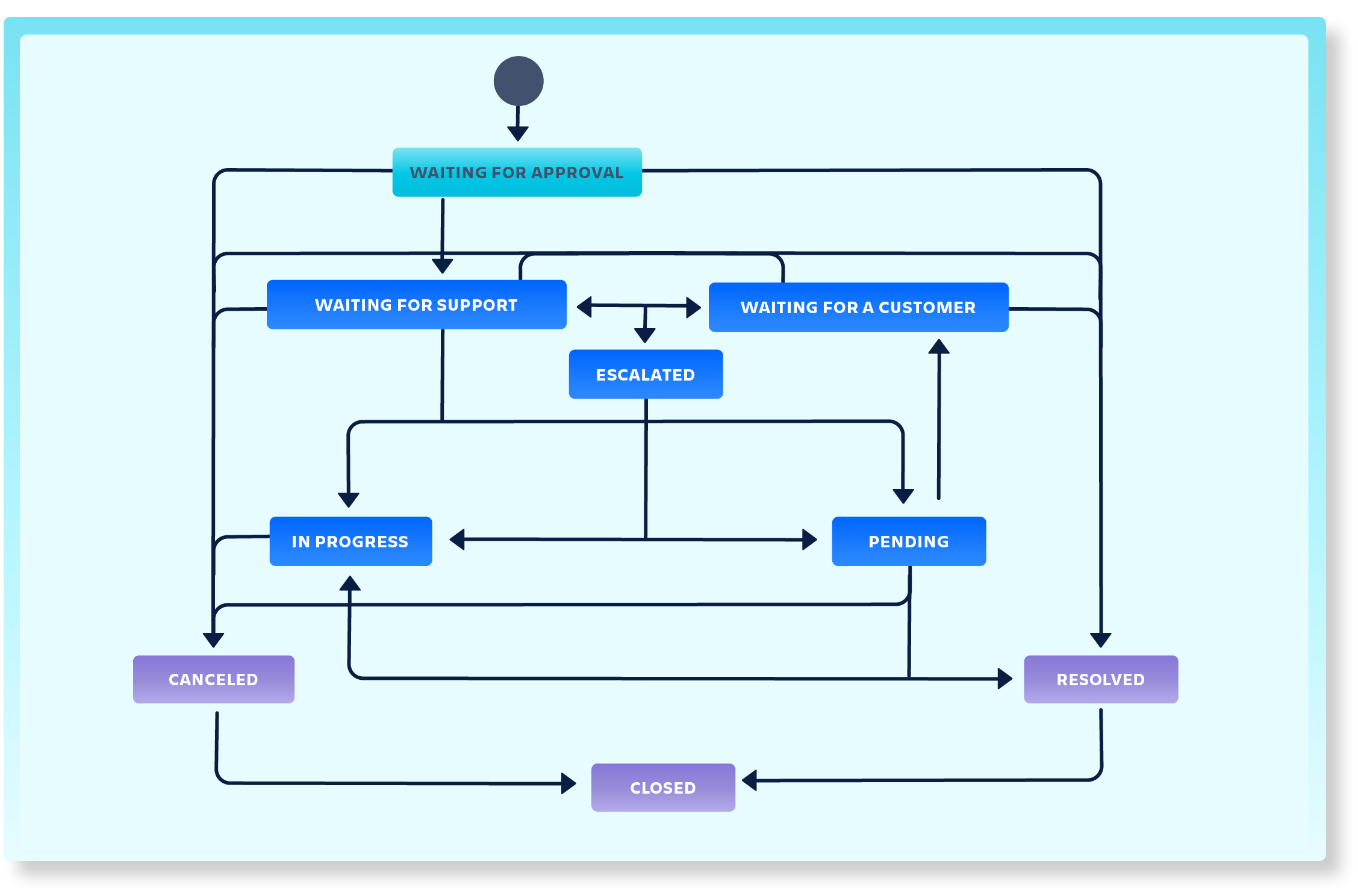
Workflow configuration
Below you will find some typical workflows in JSM for business teams. Make sure to implement the findings that you came up with during the discovery work. Even though there are good templates to start with, ono-size-fits-all, and you need to make the workflow fit your purposes and adapt it to your organizational needs.
Questions
Regular questions from the portal only need a very basic workflow.
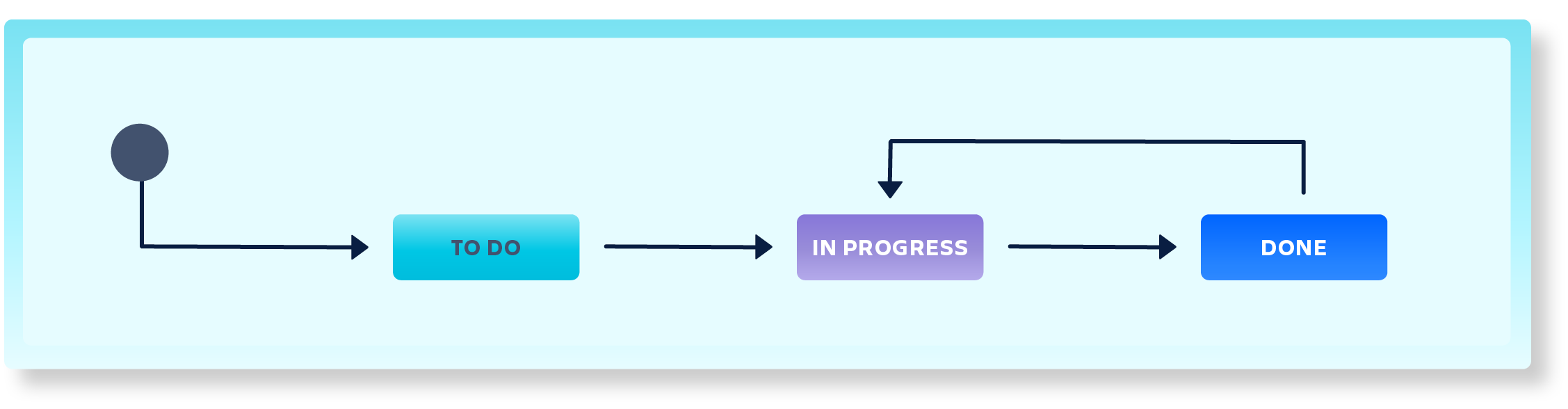
Requests
This is a simple workflow that can be used for various requests.
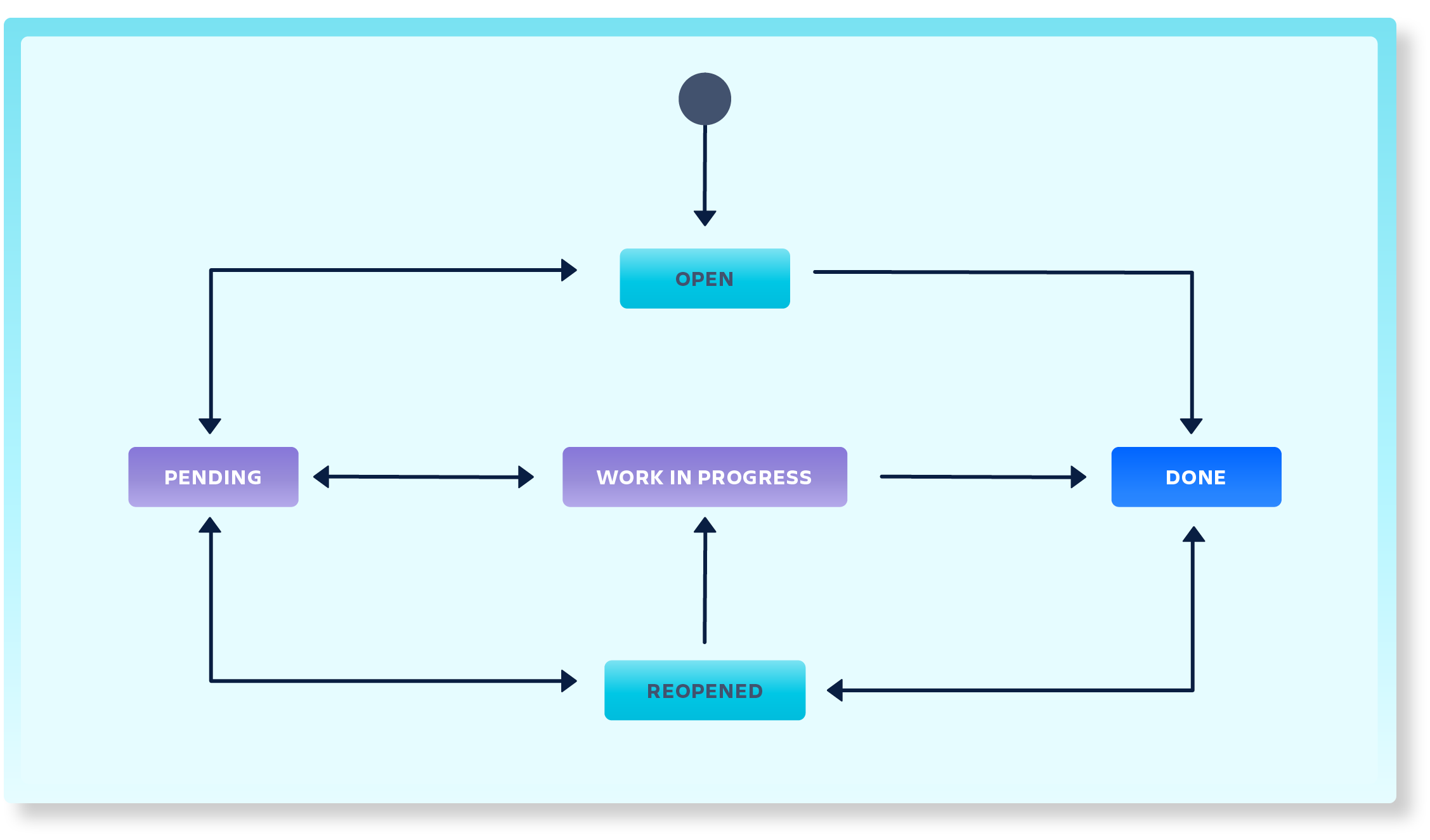
Requests with approvals
The following request is a typical approval flow where the responsible approver will be notified about a new approval request, and the agent won’t need to keep track of the issue until it has been approved and is ready to be worked on (Waiting for Support):
Here are some common approval types that business teams may have:
- Approvals that are time or cost-related: The manager is the one that usually approves the ticket. Examples can be when ordering a new device, purchasing a new license for a product or service, or creating a leave request.
- Approvals that are access related: This is usually handled by the product or application team and involves questions about why the user needs access.
- Pre-approved tickets: The ticket is automatically transitioned through the approval status if the conditions are met.
- Approvals for making changes: This usually involves a group of people (CAB) where one or several users need to approve.
You can, of course, also mix and match these and have several approval steps in your workflow.
You may use information in your Asset inventory to assist with the approval process. For example, by configuring your workflow to use the Manager of the user to be responsible for approving the ticket or by using the Service approval team related to the ticket.
Help center and portal configuration
HR portal example
Marketing portal example

Additional tips and tricks
To go beyond what is available out of the box and expand the Atlassian tools' functionality, look at the powerful Atlassian Marketplace for apps.
Business teams often work with partners/customers outside of their organization. For example, when procuring new devices and booking logistics for business trips. Tracking this can be a hassle. For this, we recommend apps that enhance the Email experience, like: Email This Issue or Enterprise Mail Handler.
HR teams can benefit from posting information about upcoming salary reviews, new employees, etc., using the knowledge base functionality of JSM. Finance teams can add information about upcoming changes to how representation should be accounted for and so on. IT Operations can plan suitable deployment time slots in the Marketing applications when there are no events - this can be done by looking into Team calendars in Confluence together with the Change calendar.
Consider that tickets created from mail cannot be categorized like an issue created using a request form in the Service Portal. Tickets created via email can be grouped under ‘General / Other’ requests, where default SLAs can apply. So consider having separate SLAs for tickets created via mail and tickets created directly in the portal.
Other use cases
Was this content helpful?
Connect, share, or get additional help
Atlassian Community